Jump statements in C :
C has four statements that perform an unconditional branch: return, goto, break and continue. Of these, you can use return and goto statements anywhere in the program. We can use a break and continue statements in conjunction with any of the loop statements.
1. break
2. continue
3. return
4. goto
break statement: The break statement has two uses. One is, to terminate a case in a switch statement. The second one is to immediate termination of a loop. When a break statement is encountered in a loop, the loop is immediately terminated, and program control resumes at the next statement following the loop.
syntax:
for ( ...... )
{
//code to execute
break ;
}
Flow chart:
Example: Program for break statement in C.
Exit(): Just as you can break out of a loop you can break out of a program by using the standard library function exit(). The exit function requires the header <stdlib.h>
syntax: void exit(int return code)
The value of the return code is a return to the calling process, which is usually the operation system. Zero is commonly used as a return code for normal program termination. Other arguments are used to indicate some sort of error.
Example: Program for exit statement in C.
Program:
Output:

continue: The continue statement skips some lines of code inside the loop after the continue statement and continues with the next iteration. It is mainly used for a particular condition so that we can skip some part of the code.
syntax: // loop code
continue ;
//statements [controller will skip this code based on the condition]
flow chart:
Example: program for continue statement in C.
return: The return statement is used to return a value from the function. it causes execution to return to the point at which the call to the function was made. A return with a value can be used only in a function with a non-void return type.
syntax: return expression;
Example: function with return statement :
int fun()
{
// code to be executed
return value; // value will be returned to the calling function
}
function without return statement :
void fun()
{
// code to be executed
}
we will discuss more functions in upcoming topics.
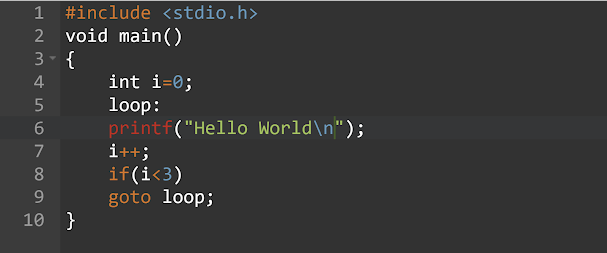
goto: The goto statement requires a Label for operation. A Label is a valid identifier followed by a colon. The Label must be in the same function as the function uses it, you cannot jump between the functions.
syntax: label name :
// set of code
goto label name;
Example: Program for goto statement in C.
Program:
Output:
The break statement exits only one loop, a goto statement may be used to exit a loop from a nested loop. The goto statement is executed until the condition is false.
prev<---loops in C Next Topic--->methods in C













No comments:
Post a Comment